Fast working memory in the generation change
A chronology of fast memory with its increasing clock speeds from SDR to DDR5.
DDR-SDRAM memory at a glance
DDR RAM is mostly used as main memory. This designation makes it clear that it is a memory that contains the programs or parts of programs that are currently being executed and the required data. Memory modules in the DIMM format are mainly used in servers and PCs. SO-DIMM are used in notebooks.

Technical terms: DDR-SDRAM at a glance
DDR RAM: Double Data Rate
In DDR RAM, unlike the older SDR RAM, the data bits are transferred on the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. Equivalently, there are also procedures with fourfold (Quadruple Data Rate, QDR) or even eightfold (Octal Data Rate, ODR) data rate.
DIMM: Dual Inline Memory Module
In contrast to single inline memory modules (SIMMs), DIMMs, i.e. double-row memory modules, have connection contacts on the front and on the back of the circuit board, which carry different signals. Usually, memory chips are also installed on both sides.
ECC Working memory: Error-Correcting Code Memory
ECC means that the memory module has the ability to detect and correct 1 and 2 bit errors if the motherboard and BIOS support it.
FBDIMM Working memory: FB = Fully Buffered Dual In-Line Memory Module
FBDIMM are DRAM modules in which the memory chips are not directly connected to the computer, but which contain another component for control (the buffer). They are considered the successor to Registered modules, both of which are primarily used for server and workstation applications.
RDIMM Memory: RDIMM = Registered Dual In-Line Memory Module
Register module refers to a type of memory module that is often used in the main memory of servers and workstations. The goal of the technology is to reduce the electrical load on the memory controller with additional registers, thereby increasing the number of memory chips that can be connected, as well as data integrity.
UDIMM Memory: UDIMM = Unregistered Dual In-Line Memory Module
This type of memory, on the other hand, does not use any additional registers. It is therefore more frequently installed in home PCs for economic reasons.
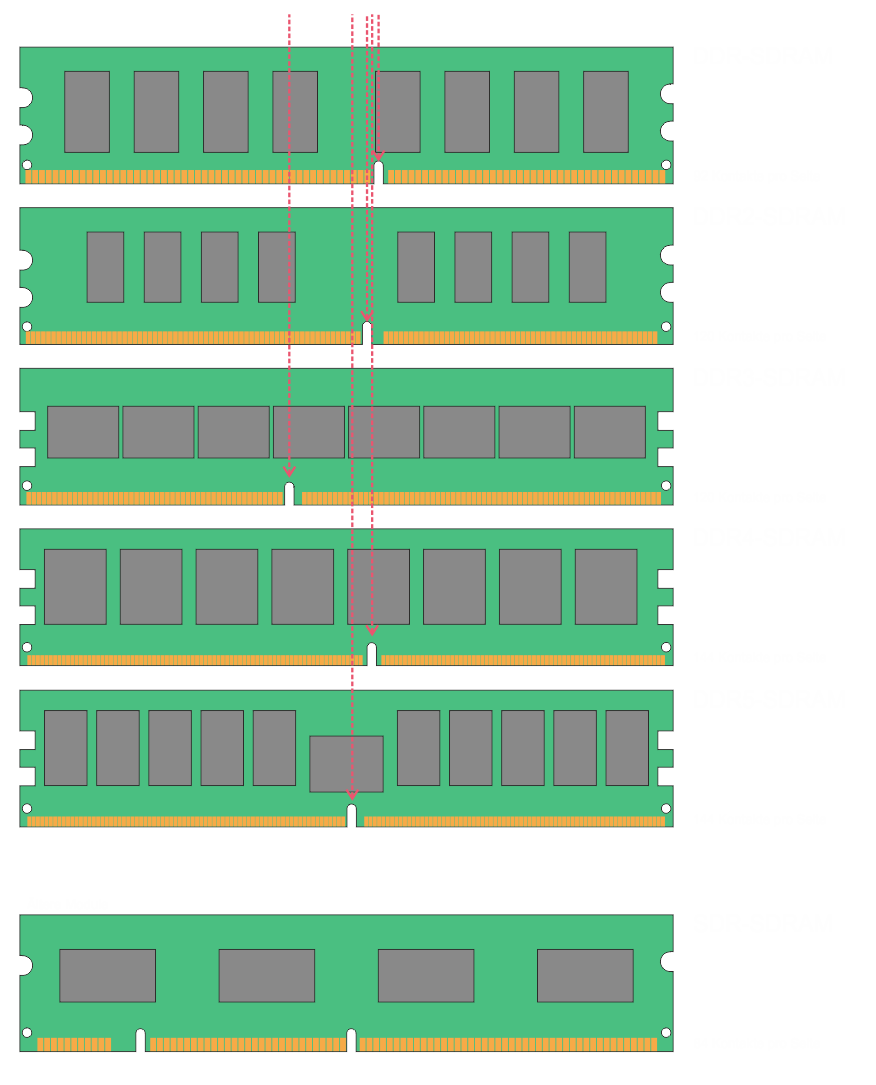
Designs of DDR SDRAM
Identifying RAM modules: Small differences with a big effect:
SDR vs. DDR vs. DDR2 vs. DDR3 vs. DDR4 vs. DDR5 SDRAM