RAID 6 vs RAID 10 with four drives
Parity vs. mirroring: Which RAID for which application?
RAID 6 versus RAID 10
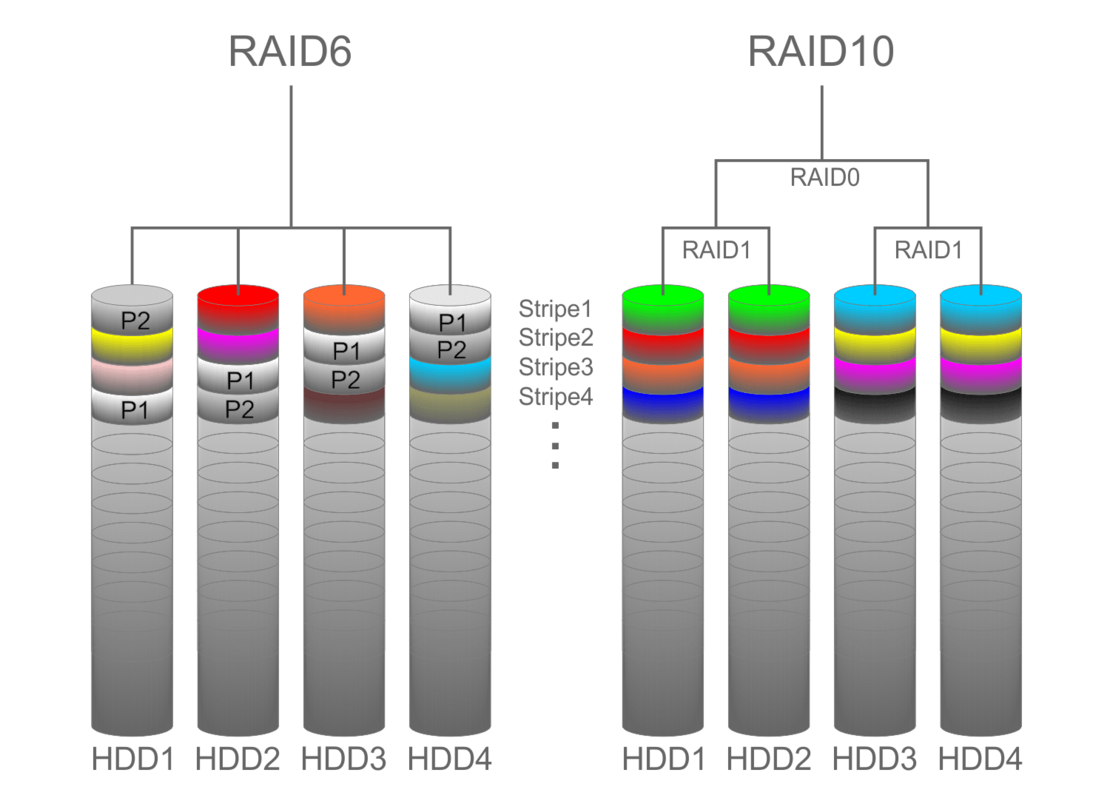
Data security and risk of disc failure
With RAID 10, the failure of a drive can be tolerated without any problems, as the data remains available on the corresponding mirror disc. However, the risk increases in the event of a second drive failure: in this case, there is a 33 per cent probability of data loss if the second failed drive is the mirror drive of the first.
In contrast, RAID 6 offers greater data security. Even if two disks fail, no data is lost as the parity data enables recovery. The risk of data loss in the event of two disk failures is therefore 0% with RAID 6. RAID 6 is therefore more robust against multiple failures than RAID 10.
Writing and reading performance
RAID 10 has an advantage in terms of write performance, as no parity data has to be calculated. The data is simply copied to the mirror disc, which is usually faster. With RAID 6, however, additional computing power is required to create and save the parity data, which can reduce the write speed.
RAID 10 also performs better in terms of read performance, as the data can be read from all four disks simultaneously. RAID 6, on the other hand, only reads the data from two disks, as the parity data is not required. However, the actual performance of both systems depends heavily on the performance of the controller. A powerful controller can reduce the performance differences between the RAID levels.
Recovery time after a disc failure
Recovery after a disk failure is comparatively simple and fast with RAID 10. The data is copied from the mirror disc, which requires less time and resources. With RAID 6, on the other hand, rebuilding is more complex.
Here, the data of the failed disk must be reconstructed from the parity data and the remaining disks, which is both more time-consuming and more resource-intensive. RAID 10 therefore offers shorter recovery times than RAID 6.
RAID 10 is therefore ideal when performance and fast recovery are crucial, but with a higher risk of multiple failures. RAID 6, on the other hand, offers greater data security, especially in the event of multiple disk failures, but at the expense of performance and recovery time.

