Thunderbolt 5: The new universal standard
Thunderbolt 5 is just around the corner
One for all: image signals, energy & networking
Thunderbolt 5 is the latest standard for connecting devices such as laptops, external data storage devices or monitors. It works via USB-C and combines the protocols of USB2, USB3, USB4, DisplayPort and PCIe. This technology brings numerous improvements that offer major advantages, especially in areas such as gaming, video editing and data backup.
Review of Thunderbolt 3
A standardized connector was introduced for the first time in 2015 with Thunderbolt 3: USB-C. This made the connection more flexible, as the same port could be used for Thunderbolt devices and USB devices.
Thunderbolt 3 achieved a speed of up to 40 Gbit/s, which was a huge leap at the time. Thunderbolt 3 particularly showed its strengths with external SSDs or when connecting multiple 4K monitors.
The power supply of up to 100 watts made it possible to charge laptops via the same connection that transmits data.
What makes Thunderbolt 5 better?
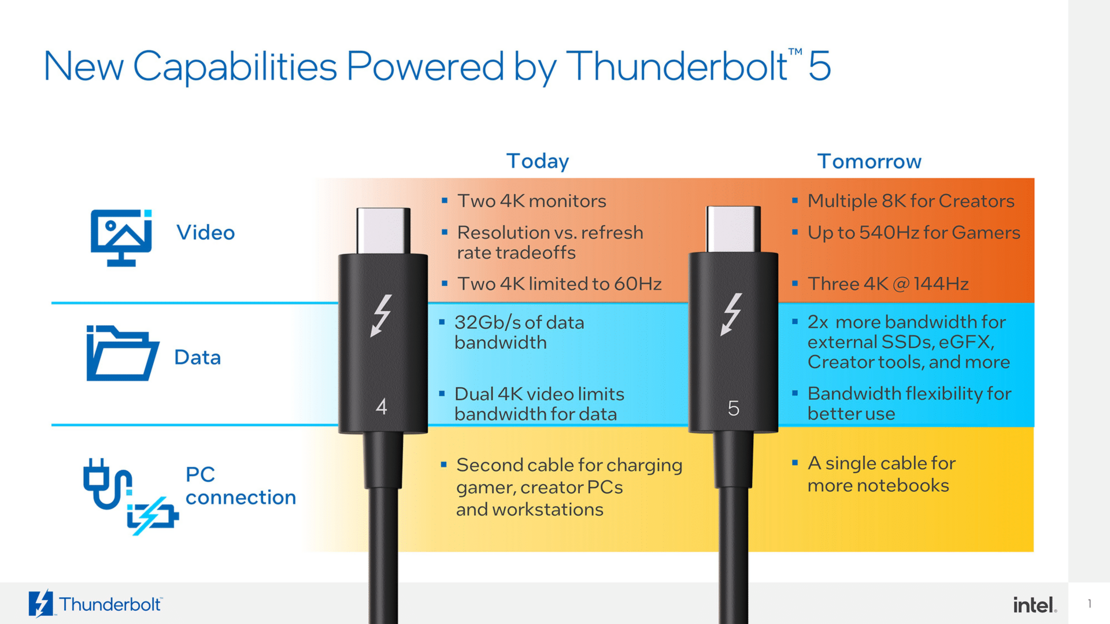
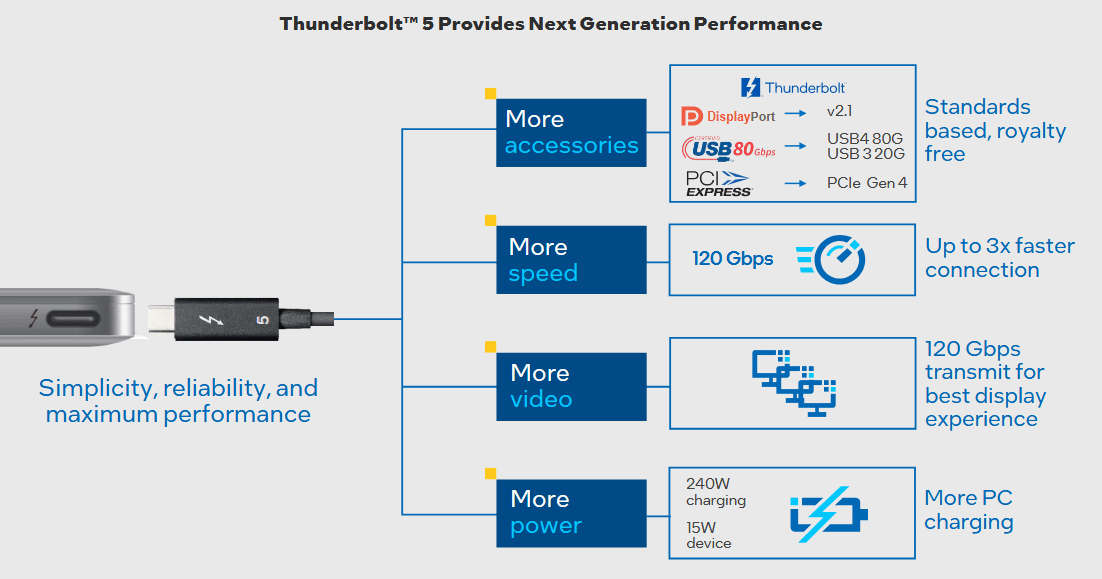
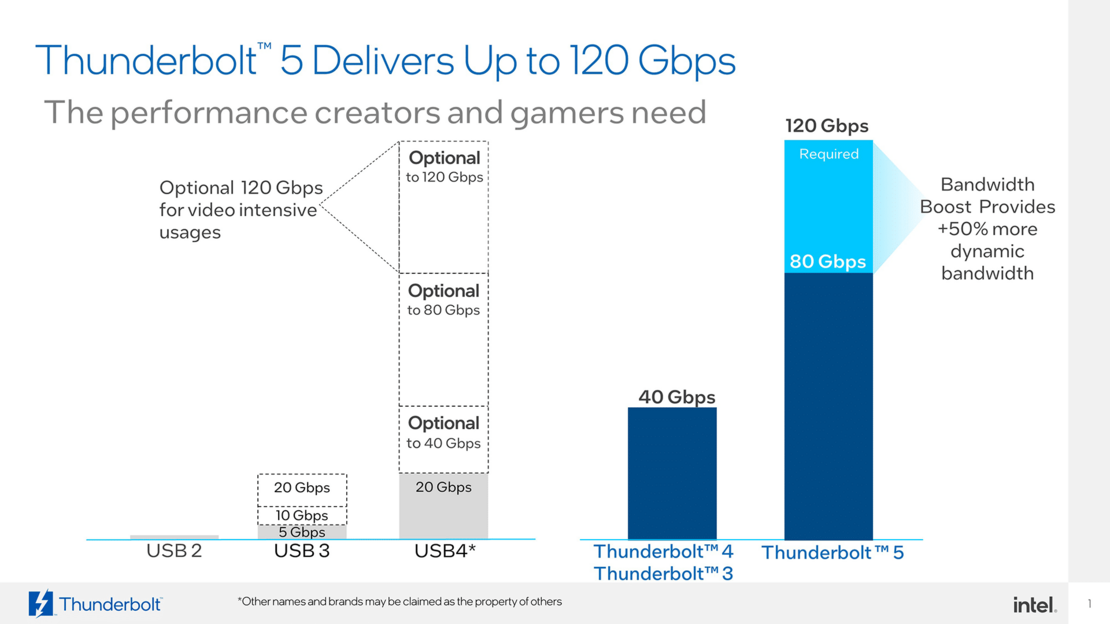
Thunderbolt 5 raises the bar even higher. With a speed of up to 120 Gbit/s, the new standard is three times faster than Thunderbolt 3. This is made possible by a technology called "Bandwidth Boost". Data channels are used more efficiently so that more data can be transferred simultaneously. The controller allows asymmetric timing in the direction of the client. This results, for example, in a maximum speed of 120 Gbit/s in the outward direction and 40 Gbit/s in the opposite direction.
Another advantage: Thunderbolt 5 offers support for the latest displays with high resolutions. 8K monitors or multiple 6K screens can be operated without delay. The power supply has also been increased to up to 240 watts , which supports particularly powerful devices such as gaming laptops or professional cameras.
Similarities and differences to USB
Thunderbolt 5 and USB share the same connector, the USB-C port. This means that Thunderbolt ports are backwards compatible with USB devices. Regardless of whether a USB hard disk or a printer is connected, they work without any problems. The difference lies in the performance. While USB 3.2 achieves a maximum speed of 20 Gbit/s, Thunderbolt 5 transmits up to 120 Gbit/s.
Another difference: Thunderbolt allows several devices to be connected in a chain. An example would be a laptop connected to a monitor via Thunderbolt, which in turn connects an external hard disk. USB does not support this "daisy chaining" function.